What’s the Difference Between Near-Infrared and Far-Infrared Heat Therapy?
Share
Introduction
In the world of electromagnetic radiation, infrared light plays a crucial role in various applications, and two distinct segments of the infrared spectrum stand out: Near-Infrared (NIR) and Far-Infrared (FIR). In this post, we'll explore these two segments, shedding light on their differences in heat penetration within biological tissues and their diverse applications. As we delve into the details, you'll discover why far-infrared, or FIR, is often considered superior for certain therapeutic and wellness applications.
Understanding Near-Infrared (NIR)
Near-Infrared (NIR) radiation falls within the wavelength range of 700 nanometers (nm) to 1,400 nm. NIR is known for its unique characteristics and applications:
Characteristics of NIR
NIR radiation has shorter wavelengths, making it closer to the visible light spectrum. It interacts with biological tissues primarily on the surface and at shallow depths.
Sources and Applications of NIR
NIR radiation is employed in various medical and diagnostic applications, including spectroscopy and imaging. It's also used in communication devices and remote controls.
NIR Heat Penetration
NIR radiation is known for its limited heat penetration. It primarily affects the skin and superficial tissues, leading to surface heating effects. For example, NIR is used in phototherapy for skin treatments and rejuvenation.
However, the limited penetration depth of NIR makes it less suitable for reaching deeper tissues in the body, which is often necessary in therapeutic and wellness applications.
Understanding Far-Infrared (FIR)
Far-Infrared (FIR) radiation falls within the longer wavelength range of 3,000 nanometers (nm) to 1 millimeter. FIR has distinct characteristics and applications:
Characteristics of FIR
FIR radiation is characterized by its longer wavelengths, placing it in the infrared spectrum. FIR interacts with biological tissues at greater depths.
Sources and Applications of FIR
FIR radiation is commonly used in applications like FIR saunas and FIR therapy. It is also employed in materials science for various purposes.
FIR Heat Penetration
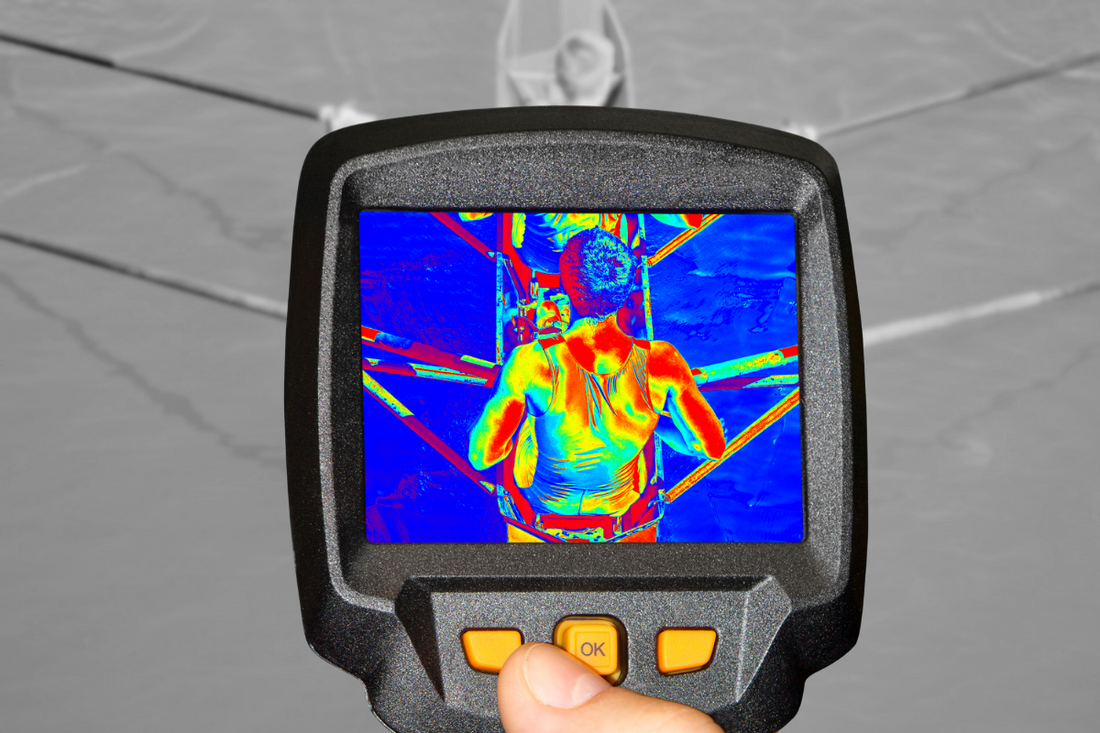
One of the key advantages of FIR radiation is its ability to penetrate deeper into the body. It can reach several centimeters below the skin's surface, affecting subcutaneous tissues, muscles, and even joints. FIR generates heat within the body, making it an ideal choice for therapeutic and wellness applications.
Conclusion: Why Far-Infrared is Superior
While both Near-Infrared (NIR) and Far-Infrared (FIR) have their respective applications, it's clear that FIR holds a superior position when it comes to heat penetration within biological tissues. FIR's ability to reach deeper tissues, including muscles and joints, makes it the preferred choice for therapeutic and wellness applications. So, when considering applications that require deeper heat penetration, such as pain relief, relaxation, and improved circulation, far-infrared is the superior choice.
In summary, this post has shed light on the thermal divide between NIR and FIR radiation. The unique characteristics of FIR, including its superior heat penetration, make it a compelling option for those seeking the benefits of infrared technology in various domains. When investing an infrared technology, choose one with FIR, like that found in the XOTHRM SmartPad, for optimal benefits.
